Supported Frameworks
On this page you can find overview of annotations supported by Miredot. Most JAX-RS, Spring MVC and Jackson annotations are fully supported. Although Miredot only outputs Json documentation, a subset of JAXB annotations are supported as well to the extent that they are also useful to specify Json output. Additional annotations will be supported in later versions. Furthermore, Miredot provides a number of custom annotations (see manual).
- JAX-RS Annotations
- JAXB Annotations
- Spring-MVC Annotations
- Security Annotations
- Jackson Annotations
- RestEasy Annotations
- Validation Annotations
JAX-RS Annotations
JAX-RS annotations on interfaces define the REST service endpoints.
@Path
Identifies the URI path that a resource class or class method will serve requests for.
Fully supported, except searching in viewer on wildcard paths that may contain slashes.
@GET, @PUT, @POST, @DELETE and @HEAD
HTTP method. Fully supported.
@Produces and @Consumes
Defines the media type(s) that the resource methods can produce / consume. Fully supported.
@PathParam, @QueryParam, @MatrixParam, @HeaderParam, @CookieParam, @FormParam, @BeanParam
Binds value(s) of a HTTP request to a resource method parameter. Fully supported.
@DefaultValue
Defines the default value of request metadata. Its value is shown next to the parameter type. Fully supported.
@Context
Annotation used to inject information into a class field, bean property or method parameter. Fully supported (ignored).
@ApplicationPath
Sets the base URI for all classes annotated with @Path. Fully supported.
JAXB Annotations
Miredot supports a number of JAXB annotations to the extent that these annotations are useful in the context of Json serialization. Most of the JAXB annotations supported by Jackson are also supported by Miredot.
@XmlAccessorType
Similar to @JsonAutoDetect, but less flexible. Alters which members get added to the payload.
Possible settings are FIELD (only and all fields are added), PROPERTY (only public getters
and setters are added), PUBLIC_MEMBER (default, all public members are added) and NONE (nothing
is added). Fully supported.
@XmlAttribute
Similar to @JsonProperty. The annotated field or method gets added to the payload. It is possible
to alter the property's name with the name parameter. A property can also be marked as required.
Fully supported.
@XmlElement
Similar to @JsonProperty. The annotated field or method gets added to the payload. It is possible
to alter the property's name with the name parameter. A property can also be marked as required.
The type property for use in polymorphic handling is currently not supported by Miredot, otherwise
the annotation is fully supported.
@XmlElementRef
Alters the name of the annotated field or method. The altered name comes from the @XmlRootElement
annotation that is put on the class of the property's type. If no @XmlRootElement is present the
@XmlElementRef annotation has no effect. Fully supported.
@XmlTransient
Similar to @JsonIgnore, but without the possibility to turn it off again (in a derived class).
Fields or methods annotated with @XmlTransient are not added to the payload. Fully supported.
@XmlType
Only the propOrder parameter is supported and is similar to @JsonPropertyOrder. Used to order the
properties in the payload.
@XmlValue
Renames the annotated field or method to "value". Fully supported.
Spring-MVC Annotations
Spring-MVC annotations on interfaces define the REST service endpoints.
@RequestMapping
This annotation can contain multiple elements. Miredot supports the following elements:
- value (defines the URI of your REST Interface)
- method (HTTP Method of your REST Interface)
- consumes (Consumable media types)
- produces (Producable media types)
IMPORTANT Miredot does not yet support multiple
values for the value and method elements of the @RequestMapping annotation.
@RequestParam
Annotation which indicates that a method parameter should be bound to a web request parameter.
IMPORTANT Miredot only supports the value and
defaultValue attributes on the @RequestParam annotation.
@PathVariable
Annotation which indicates that a method parameter should be linked to a URI variable. Fully Supported.
When a value isn't explicitly given, Miredot assumes the parameter name of the method is used as the name for the
@PathVariable. Miredot's code analysis can detect when this name is not found in the URI
template (given by the value element of the @RequestMapping annotation).
@ResponseStatus
On a method, this annotation indicates the HTTP status code it should return when the method is executed successfully. It can also be used at class-level on exception classes to ensure a certain HTTP status code is returned when the annotated exception is thrown. Miredot fully supports both usages of this annotation.
Since Miredot also offers its own configuration section for the documentation of status codes,
it is possible that both @ReponseStatus annotations and Miredot's own configuration are simultaneously present.
Regardless of annotations, Miredot will always display those status codes that are configured to be shown for either all
interfaces or all interfaces with predefined HTTP operations (GET/PUT/POST/DELETE). However, if the Miredot
documentation maps a certain exception to an HTTP status code, and that exception class is also annotated with the
@ResponseStatus annotation, the @ResponseStatus takes precedence.
@RequestHeader
On a method parameter, this annotation indicates that the parameter should be injected with a value from the request headers.
Spring-MVC also supports this annotation on a parameter of type Map<String, String>, MultiValueMap<String, String> or HttpHeaders. In this case all headers are injected. This usage is ignored by Miredot.
Security Annotations
@RolesAllowed, @PermitAll
Annotations used to control authorization.
Jackson Annotations
Jackson annotations change the (de)serialisation of the in- and output of the REST services. Miredot takes these into account for the API visualization. How these annotations are supported is described below.
For a more detailed description of the Jackson annotations, see the jackson-annotations Javadoc.
@JsonIgnore
Annotation that indicates that the annotated method or field is to be ignored for (de)serialization. Fully supported.
@JsonIgnoreProperties
Annotation on class or field to prevent specified fields from being (de)serialized. Only annotation on class supported.
@JsonProperty
Transforms any non-static method into getter or setter, independent of method name or visibility. The method will be a getter/setter if its signature matches that of a getter/setter. Transforms any non-static field into logical property, independent of visibility. Changes the property name that is used externally for (de)serialization. Fully supported.
@JsonValue
Annotation on method that indicates that the result of the annotated "getter" is to be used as the single value to serialize for the instance. The return type of this method is used in Miredot to document the output of a service. Fully supported.
@JsonCreator
Annotation that can be used to define constructors and factory methods as one to use for instantiating new instances of the associated class. Supported: property-based creators (on constructor or on static class). Their properties are added to the JSON input visualization of a service. Not supported: delegate-based creators in which JSON is passed to a single-argument creator. We don't know the property names, so we cannot add them to the JSON visualization.
@JsonAutoDetect
Class annotation that can be used to define which kinds of methods are to be detected by auto-detection. Fully supported.
Auto-detection can be changed globally by specifying visibility in your project pom.
@JsonTypeInfo, @JsonSubTypes & @JsonTypeName
@JsonTypeInfo describes if and how type information is used with JSON (de)serialization. Currently only
JsonTypeInfo.Id.NAME, JsonTypeInfo.Id.CLASS and JsonTypeInfo.Id.MINIMAL_CLASS are supported.
JsonTypeInfo.Id.NONE and JsonTypeInfo.Id.CUSTOM use the simple name of the class.
JsonTypeInfo.Id.CLASS can be used with or without @JsonSubTypes annotations. In the latter case, Miredot documents
all derived classes in your project.
@JsonTypeName is used for binding a logical name to the annotated class.
Fully supported.
@JsonPropertyOrder
Annotation that allows you to specify the serialization order of the fields in JSON. Fully supported.
@JsonUnwrapped
Annotation on a property of a transfer object that unwraps all its fields in that transfer object directly. Fully supported.
@Bean
Easily reuse common groups of parameters. Partially supported.
RestEasy Annotations
Support for these annotations is automatically enabled when choosing JAX-RS as the REST Framework in the Miredot configuration (for more information see Choosing a Rest Framework).
@GZIP
Can be applied to a REST resource to indicate its content is gzipped when sent to the client.
@Form
Allows you to re-use any @*Param annotation within an injected class. Similar to @Bean
Validation Annotations
Annotations defined in the package javax.validation.constraints. Used for validating input.
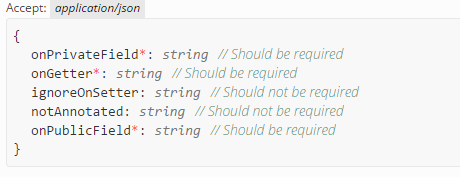
@NotNull
Can be applied to a field or getter of a JSON payload. It indicates that the field is required. Miredot will document this by placing a red asterix where applicable. For an example, check out the screenshot below.